Vitamin K
Vitamin K (aka Vitamin K1) is a fat-soluble vitamin (technically known by the INCI name phytonadione). Products rich in vitamin K aid in your skin’s healing process if it’s been compromised as it supports the skin’s natural barrier function, so any cuts or bruises will thank you. A minimum 1% concentration of vitamin K1 has been shown in animal studies to positively influence wound healing by hastening the natural process damaged skin undergoes as it works to repair itself. I
Vitamin K refers to structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation (K from Koagulation, German for "coagulation") or for controlling binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. The complete synthesis involves final modification of these so-called "Gla proteins" by the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase that uses vitamin K as a cofactor.
| Vitamin K | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
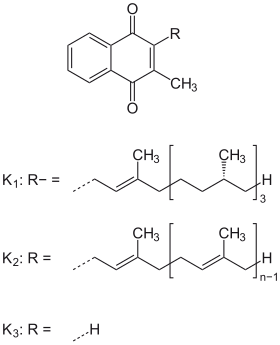 Vitamin K structures. | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Use | Vitamin K deficiency, Warfarin overdose |
| ATC code | B02BA |
| Biological target | Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase |
| Clinical data | |
| Drugs.com | Medical Encyclopedia |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D014812 |
| In Wikidata | |
Vitamin K is used in the liver as the intermediate VKH2 to deprotonate a glutamate residue and then is reprocessed into vitamin K through a vitamin K oxide intermediate. The presence of uncarboxylated proteins indicates a vitamin K deficiency. Carboxylation allows them to bind (chelate) calcium ions, which they cannot do otherwise. Without vitamin K, blood coagulation is seriously impaired, and uncontrolled bleeding occurs. Research suggests that deficiency of vitamin K may also weaken bones, potentially contributing to osteoporosis, and may promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.
Chemically, the vitamin K family comprises 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (3-) derivatives. Vitamin K includes two natural vitamers: vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and vitamin K2 (menaquinone). Vitamin K2, in turn, consists of a number of related chemical subtypes, with differing lengths of carbon side chains made of isoprenoid groups of atoms. The two most studied ones are menaquinone-4 (MK-4) and menaquinone-7 (MK-7).
Vitamin K1 is made by plants, and is found in highest amounts in green leafy vegetables, because it is directly involved in photosynthesis. It is active as a vitamin in animals and performs the classic functions of vitamin K, including its activity in the production of blood-clotting proteins. Animals may also convert it to vitamin K2, variant MK-4. Bacteria in the gut flora can also convert K1 into MK-4. All forms of K2 other than MK-4 can only be produced by bacteria, which use these during anaerobic respiration. Vitamin K3 (menadione), a synthetic form of vitamin K, was used to treat vitamin K deficiency, but because it interferes with the function of glutathione, it is no longer used this way in human nutrition.









