Ornithine
Ornithine is an amino acid that plays a central role in the urea cycle, a crucial metabolic process that helps the body eliminate ammonia, a toxic byproduct of protein metabolism. Unlike most amino acids, ornithine is not used to build proteins. Instead, it serves primarily as an intermediary in the urea cycle, facilitating the conversion of ammonia into urea, which is then excreted from the body through urine.
The urea cycle is a series of biochemical reactions that occur mainly in the liver. Ornithine combines with ammonia and carbon dioxide to form citrulline and eventually urea, the body’s main vehicle for removing nitrogenous waste. This cycle is essential for maintaining the nitrogen balance in the body and for preventing the accumulation of ammonia in the blood, which can be detrimental to the central nervous system and lead to serious health issues.
In addition to its role in the urea cycle, ornithine is also involved in other metabolic pathways. It is a precursor to arginine, another amino acid that has various physiological roles, including the production of nitric oxide, a vital compound for blood vessel dilation and improved blood flow. Ornithine supplementation has been studied for potential benefits in areas such as wound healing, exercise performance, and promoting healthy sleep patterns, owing to its role in these metabolic processes.
Ornithine’s importance in metabolism and potential health benefits has made it a subject of interest in nutritional science and supplement industries, where it is marketed for various health claims, including enhancing liver function, supporting detoxification, and improving athletic performance. However, it’s always important to approach supplementation with caution and seek advice from healthcare professionals.
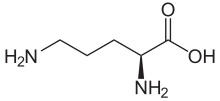
Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic α-amino acid that plays a role in the urea cycle. Ornithine is abnormally accumulated in the body in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. The radical is ornithyl.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
L-Ornithine
| |
| Other names
(+)-(S)-2,5-Diaminovaleric acid
(+)-(S)-2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.665 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Ornithine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 132.16 g/mol |
| Melting point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.94 |
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+11.5 (H2O, c = 6.5) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |









