Glycine
Glycine is an essential amino acid, essential to the human body because it is an important constituent of proteins and is used in the production of certain neurotransmitters. It is the simplest amino acid, with the simplest chemical structure and the smallest side chain. Glycine is an important component of collagen, which is important for tissue formation and the maintenance of healthy bones, skin and joints. It also helps to regulate blood sugar levels and is important for proper muscle and nerve function. Glycine is found naturally in a variety of foods, including meat, dairy, beans, nuts and seeds.
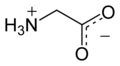
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; /ˈɡlaɪsiːn/ (![]() listen)) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐CH2‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a Clostridium tetani infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction.
listen)) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐CH2‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a Clostridium tetani infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction.
| |||
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Aminoacetic acid
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-Aminoethanoic acid | |||
| Other names
Aminoethanoic acid, Glycocol
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | Gly, G | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.248 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H5NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 75.067 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 1.1607 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 233 °C (451 °F; 506 K) (decomposition) | ||
| 24.99 g/100 mL (25 °C) | |||
| Solubility | soluble in pyridine sparingly soluble in ethanol insoluble in ether | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.34 (carboxyl), 9.6 (amino) | ||
| -40.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Pharmacology | |||
| B05CX03 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
2600 mg/kg (mouse, oral) | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Glycine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom.