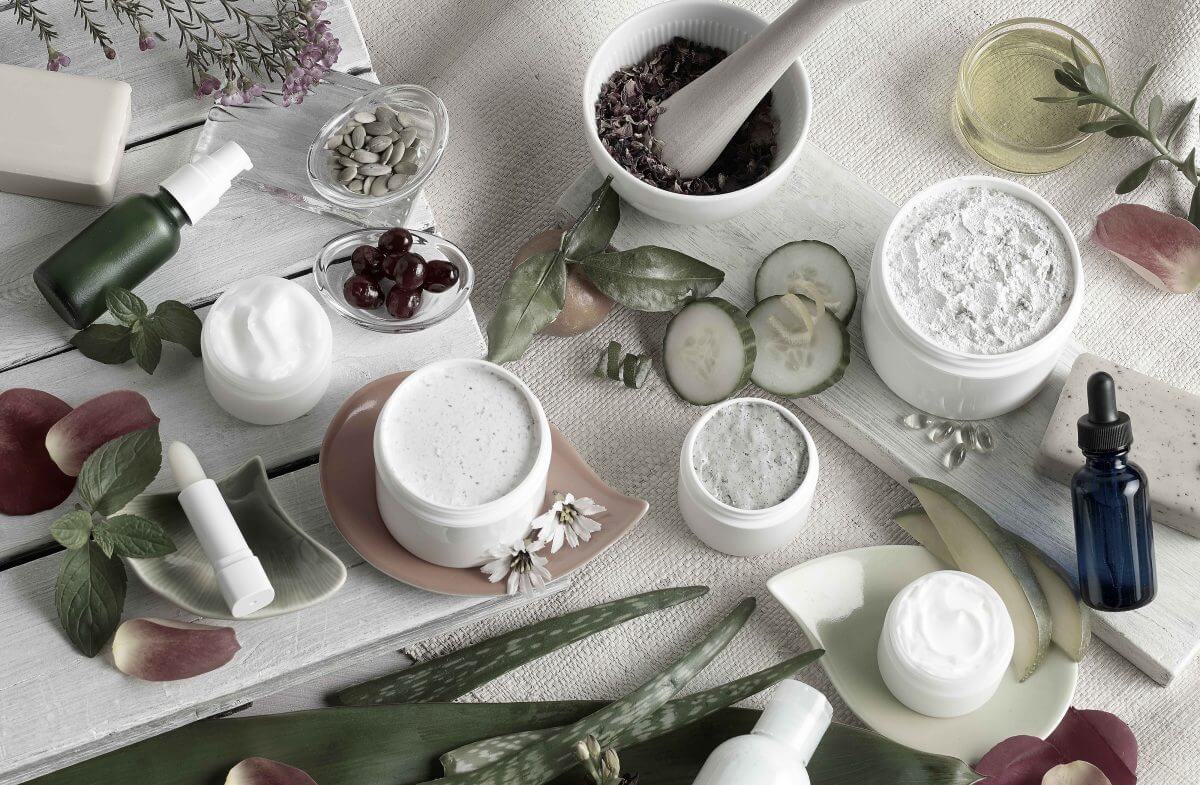
Chondrus Crispus
Chondrus crispus is the material obtained from the whole alga, chondrus crispus, gigartinacea (algae).
It is a type of algae extract coming from the algae commonly called Irish moss or red seaweed. It is rich in carrageenan, a natural polymer that acts as a gelling, thickening and stabilizing agent.
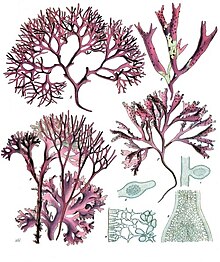
Chondrus crispus—commonly called Irish moss or carrageen moss (Irish carraigín, "little rock")—is a species of red algae which grows abundantly along the rocky parts of the Atlantic coast of Europe and North America. In its fresh condition this protist is soft and cartilaginous, varying in color from a greenish-yellow, through red, to a dark purple or purplish-brown. The principal constituent is a mucilaginous body, made of the polysaccharide carrageenan, which constitutes 55% of its dry weight. The organism also consists of nearly 10% dry weight protein and about 15% dry weight mineral matter, and is rich in iodine and sulfur. When softened in water it has a sea-like odour and because of the abundant cell wall polysaccharides it will form a jelly when boiled, containing from 20 to 100 times its weight of water.
| Irish moss | |
|---|---|
| |
| A-D Chondrus crispus ; E-F Mastocarpus stellatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Archaeplastida |
| Division: | Rhodophyta |
| Class: | Florideophyceae |
| Order: | Gigartinales |
| Family: | Gigartinaceae |
| Genus: | Chondrus |
| Species: | C. crispus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Chondrus crispus | |









